Shapes can function as a clue to identify the source and
differentiate between products of different companies. While
browsing a store shelf, consumers often identify a product by its
shape before even noticing its label. Shape marks offer a
beneficial avenue to safeguard product designs, packaging, and
containers in both Austria and the entire European Union.
Find the German version of this article below
What is a shape mark?
Shape marks or three-dimensional marks are trademarks consisting
of a three-dimensional shape. By registering a shape mark, the
appearance of a product can be protected if it is capable of
distinguishing the goods or services of one undertaking from those
of others (=acting as a trademark). You will likely recognise the
following shapes as indicating products originating from a certain
company:

EUTM 000031237
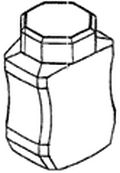
EUTM 000137406

AT 279975
Protectability of shape marks
Every physical product has a shape, but not every shape can act
as a trademark.
According to EU case law, a shape is protectable as a trademark
if it departs significantly from the norm or from the customs of
the sector concerned. In such a case it is recognised as a
trademark, i.e. as an indication of origin.
If, on the other hand, the shape is rather common, the applicant
must prove that due to intensive use the relevant public has
learned to recognise it as an indication of origin (so-called
acquired distinctiveness or secondary meaning). The European Union
Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) considered such a proof of
acquired distinctiveness necessary for the following rather common,
but due to the use distinguishable, shape of a bass or guitar
head:

EUTM 003318474
It should be noted at this point that trademarks which consist
exclusively of shapes of goods that are necessary to obtain a
technical result are excluded from trademark protection under all
circumstances, even if they have acquired distinctiveness through
use.
Representation of the shape
According to EU case law, a trademark must be presented on the
register in a clear, precise, self-contained, easily accessible,
intelligible, durable and objective manner. The competent
authorities and the public must be able to determine with clarity
and precision the subject matter of the protection afforded to the
trademark owner.
Thus, before registering a shape mark, representations should be
arranged that wholly and accurately reflect the shape. Today’s
multimedia registers allow for different types of representations
(depending on the register) such as photos, graphic
representations/sketches or 3D models (X3D).
If a representation contains elements for which no protection is
claimed, applicants may disclose this by depicting such elements in
broken lines.
Additionally, Austrian and EU trademarks can also be given
descriptions (e.g. to explain the illustrations).
Technical requirements within the Austrian and EU application
process
Currently, the Austrian Patent Office only accepts digital
submissions for shape marks if they come in JPEG file format. The
maximum file size is 2 MB. Applications may also be filed in paper
format, in which case six identical mark images on paper (max.
size: 8 x 8 cm side length) must be submitted.
The EUIPO accepts submissions in JPEG, OBJ, STL and X3D file
formats. The file size must not exceed 20 MB. To ensure a complete
view of the mark, up to six perspectives of the same shape may be
submitted in a single JPEG file (or in hard copy on an A4
sheet).
Summary
Shapes may serve as an indication of origin and distinguish
products from one undertaking from those of another. When looking
at a store shelf, consumers sometimes recognise the shape of a
product much earlier than its label. Shape marks are a good option
to protect product designs, packaging and containers in Austria and
the entire European Union. Assessing whether the shape is
protectable as a trademark and choosing appropriate representations
are extremely important when registering this type of mark.
Was sind Formmarken?
Formmarken oder auch dreidimensionale Marken sind Marken, die
aus einer dreidimensionalen Form bestehen. Dadurch kann das
Aussehen eines Produkts, das für sich auch als Marke wirken
kann, geschützt werden. Vermutlich werden Sie zB folgende
Formen als Hinweis auf die Herkunft des Produkts aus einem
bestimmten Unternehmen wahrnehmen:

EUTM 000031237

EUTM 000137406

AT 279975
Schutzfähigkeit einer Formmarke
Jedes physische Produkt hat eine Form, aber nicht jede Form ist
eine Marke.
Eine Form ist nach der Rechtsprechung dann als Marke
schutzfähig, wenn sie erheblich von der Norm oder der
Branchenüblichkeit abweicht und (daher) als Marke – dh
als Herkunftshinweis – erkannt wird.
Trifft das nicht zu, weil es sich zB um eine eher
gewöhnliche Form handelt, muss die Anmelderin nachweisen, dass
die beteiligten Verkehrskreise die Form aufgrund der intensiven
Nutzung mittlerweile als Herkunftshinweis erkennen (sog erworbene
Unterscheidungskraft bzw Verkehrsgeltung). Einen solchen Nachweis
hielt das Amt der Europäischen Union für Geistiges
Eigentum (EUIPO) etwa für folgende – eher
gewöhnliche, aber aufgrund der Nutzung zuordenbare –
Form eines Bass- bzw Gitarrenkopfes für erforderlich:

EUTM 003318474
Zu beachten ist, dass insbesondere rein technisch bedingte
Formen keinesfalls als Marke schutzfähig sind.
Abbildung der Form
Nach der Rechtsprechung muss jede Marke im Register eindeutig,
präzise, abgeschlossen, leicht zugänglich,
verständlich, dauerhaft und objektiv dargestellt werden (es
muss klar sein, für welchen Gegenstand dem Markeninhaber
Schutz gewährt wird).
Vor einer Anmeldung sollten daher Abbildungen abgestimmt werden,
die die Form korrekt und vollständig wiedergeben. In den
heutigen Multimedia-Registern sind – je nach Register –
unterschiedliche Darstellungsvarianten denkbar, wie etwa Fotos,
grafische Darstellungen/Skizzen oder 3D-Modelle (X3D).
Falls in den Abbildungen Elemente vorhanden sind, für die
kein Schutz beansprucht wird, können diese durch gestrichelte
Linien gekennzeichnet werden.
Zusätzlich können bei österreichischen und
Unionsmarken Beschreibungen hinzugefügt werden (etwa zur
Erklärung der Abbildungen).
Technische Voraussetzungen in Österreich und in der
EU
Das österreichische Patentamt akzeptiert digitale Eingaben
für Formmarken derzeit nur im JPEG-Dateiformat. Die maximale
Größe einer Datei darf 2 MB betragen. Anmeldungen
können auch in Papier erfolgen, dazu sind sechs idente
Markenbilder auf Papier (max. Größe 8 x 8 cm
Seitenlänge) einzureichen.
Das EUIPO akzeptiert Eingaben in den Dateiformaten JPEG, OBJ,
STL und X3D. Die Dateigröße darf 20 MB nicht
überschreiten. Um die vollständige Ansicht der Marke
sicherzustellen, können bis zu sechs Perspektiven derselben
Form in einer einzigen JPEG-Datei (bzw. in Papierform auf einem DIN
A4-Blatt) eingereicht werden.
Zusammenfassung
Auch Formen können als Herkunftshinweis wirken und Produkte
individualisieren – im Regal erkennen Konsumenten die Form
mitunter schon viel früher als etwa eine Beschriftung.
Formmarken bieten eine gute Möglichkeit, Produktgestaltungen,
Verpackungen und Behältnisse in Österreich und der
gesamten Europäischen Union schützen zu lassen. Die
Prüfung der Schutzfähigkeit und die passenden Abbildungen
sind bei einer solchen Markenart von großer Bedeutung.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general
guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought
about your specific circumstances.
#Shapes #Trademarks #Trademark










